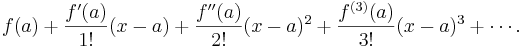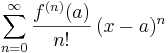Difference between revisions of "Taylor Series"
From Sean_Carver
(→New Concept: Taylor Series) |
(→New Concept: Taylor Series) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* '''Convergence:''' A function whose Taylor series converges to the function is called ''analytic''. But sometimes, as we have seen with power series generally, convergence can occur only within a radius of convergence. | * '''Convergence:''' A function whose Taylor series converges to the function is called ''analytic''. But sometimes, as we have seen with power series generally, convergence can occur only within a radius of convergence. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Example: The Taylor series for cos(x), at a = 0. Partial sums for 4 and 6 terms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:taylor45.png]] | ||
Revision as of 22:58, 14 March 2011
Review Concepts
- Sequences
- Convergence
- Infinite series
- The sequence of partial sums of an infinite series
- Power series
New Concept: Taylor Series
- Think of Taylor series as a special kind of power series, where the sequence of partial sums are meant as better and better approximations of some other function.
- The Taylor Series is derived from the function.
Definition copied, verified, and adapted from Wikipedia, this page (permanent link). See license to copy, modify, distribute.
The Taylor series of a function ƒ(x) at a is the power series
which can be written in the more compact sigma notation as
- Convergence: A function whose Taylor series converges to the function is called analytic. But sometimes, as we have seen with power series generally, convergence can occur only within a radius of convergence.
- Example: The Taylor series for cos(x), at a = 0. Partial sums for 4 and 6 terms.