Difference between revisions of "DiffEqs"
From Sean_Carver
(→Plain Bilayer Membrane) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<math> C \frac{dV(t)}{dt} = I(t) </math> | <math> C \frac{dV(t)}{dt} = I(t) </math> | ||
| + | <math> V(0) = 0 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here ''C'' is a constant (parameter), the ''capacitance'' of the membrane, proportional to area. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next ''V(t)'' is the membrane potential. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Next ''I(t)'' is the current into the membrane, with a sign such that a positive current depolarizes the cell. The sign conventions are TRICKY!!! I get confused all the time. | ||
== Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps == | == Bilayer Membrane with Na/K Pumps == | ||
Revision as of 21:28, 7 February 2009
Contents
Plain Bilayer Membrane
A plain lipid bilayer is approximately an ideal capacitor. The equation for an ideal capacitor is
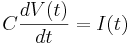
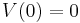
Here C is a constant (parameter), the capacitance of the membrane, proportional to area.
Next V(t) is the membrane potential.
Next I(t) is the current into the membrane, with a sign such that a positive current depolarizes the cell. The sign conventions are TRICKY!!! I get confused all the time.